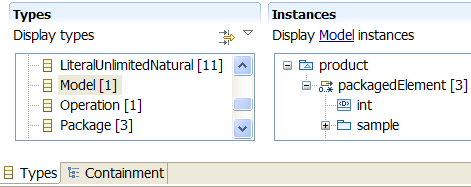
Types Vs Containment
The model editor provides two pages to navigate model elements either by types or by containment.
Filters
Filters are available to restrict model elements and features displayed in a model editor section (using the section dropdown menu).
You may for example exclude derived references, which are numerous in UML 2.1 metamodel.
Label Decorations
You may change the decorations applied on model element labels using the Label Decorations... item in the section dropdown menu.
You may for example show or hide stereotypes applied on UML 2.1 model elements.
Working Sets
Working sets define a point of view on metamodel contents. A working set is used to group together some semantically related elements. It can also be used to hide a subset of elements that are considered as non relevant for some particular modeling activity.
Search
Model elements can be queried:
- based on a textual query, in the Search dialog
- based on the selected model element, using the contextual menu, to ask for declarations or references.
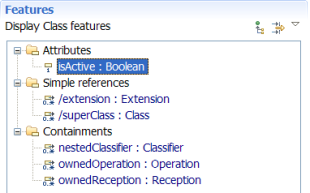
Properties
Model elements can be displayed in the Properties view, which provides support for Label Decorations, Filters, and Working Sets.
Model elements may also be displayed in a Properties dialog (Alt+Enter).
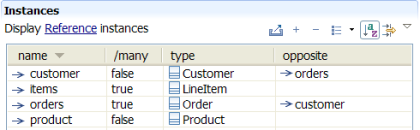
Tables
Model elements can be displayed into tables. A user may define custom table templates.
Tables can be exported into CSV file format, to view instances in Microsoft ExcelŽ for example
Editing
You can create new models, or modify the contents of existing models. You can create new model elements, modify attribute values, add new references, and delete model elements. All editing actions can be undone (CTRL+Z) and redone (CTRL+Y).
HTML Export
Both models and metamodels may be exported into HTML pages using the Services view.