Code Generation
Table of Contents
String Patterns
The code generation for this ARXF-CP has been adapted to relief you from specifying AUTOSAR details needed by the ARXF-CP,
yet allows you to modify the default behavior of the code generation.
We use string patterns which are replaced during code generation. These string patterns can be used in two locations:
- the ARXF-CP Configuration Code Generation tab
- inside a runnable, shown via the Features and Implementation tab of a runnable in an SWC or
Standard Content of an SWC
We use the following string patterns which are replaced during code generation:
- <swc> the name of the SWC the runnable, class, etc. belongs to
In Rhapsody this is the name of the class, stereotyped by CpSwc.
In AUTOSAR, this is the SoftwareComponentType
- <activeClass> the name of the active class the runnable has a dependency to, stereotyped by eventDispatcherActiveClass.
- <runnable> the name of the runnable which is specified by the tag runnableName on a CpRunnable stereotyped runnable.
- <exclusiveArea> the name of the exclusiveArea the runnable has a dependency to, stereotyped by exclusiveAreaAccess.
- <interrunnableVariable> the name of the interrunnableVariable the runnable has a dependency to, stereotyped by variableAccess.
- <prototype> the SWC prototype (RTE instance), stereotyped by ArSwcPrototype.
- <rteInstance> address of the SWC prototype.
When the SWC has the tag supportsMultipleInstantiation set to True, this is the self pointer argument to runnables. Otherwise it expands to NULL
- <self> expands to either nothing or expands to self when the SWC the runnable, class, etc. belongs to, has the tag supportsMultipleInstantiation set to True
- <access> either read, write or readwrite depending on the tag of the variableAccess stereotyped dependency towards the interrunnableVariable
Examples:
- Rte_Irv<access>_<runnable>_<interrunnableVariable>( <self> ) expanding to Rte_IrvRead_eventDispatcherSwc_rhapsodyTaskPointerSwc()
- Rte_Irv<access>_<swc>_<runnable>_<interrunnableVariable>( <self> ) expanding to Rte_IrvRead_eventDispatcherController_rhapsodyTaskPointerController( self )
- Rte_Enter_<exclusiveArea>( <self> ) expanding to Rte_Enter_mutexEventListSwc()
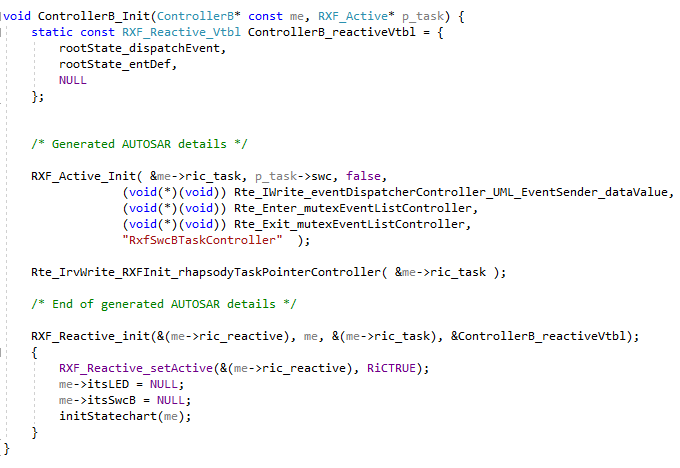
SWCs
Code is generated to initialize the critical region handlers used by the ARXF-CP and add AUTOSAR details to an internal task structure.
The RTE APIs used are function pointers which names are composed using the exclusive areas and inter-runnable variables.
To understand which inter-runnable variables belong to which runnables used for UML event dispatchers, the code generation needs two relations:
- the relation from runnable to SWC stereotyped by eventDispatcherActiveClass
to indicate the runnable is used as UML event dispatcher. See Profiles.
- the relation from runnable to interrunnableVariable stereotyped by variableAccess including if it is for reading or writing. See Profiles.
To understand which exclusive areas belong to which runnables, the code generation needs:
- the relation from runnable to exclusiveArea stereotyped by exclusiveAreaAccess
indicates the runnable is using this exclusive area for read and write. See Profiles.

Composition
The AUTOSAR rootcomposition is used for connecting the RTE instances to the Rhapsody instances of SWCs.
During code generation, for each SWC a file is generated, with the name <yourSwc>_Prototypes.c with two functions:
- <yourSwc>_getMe() which returns the address of the Rhapsody instance of the SWC prototype
- <yourSwc>_getSelf() which returns the address of the RTE instance of the SWC prototype
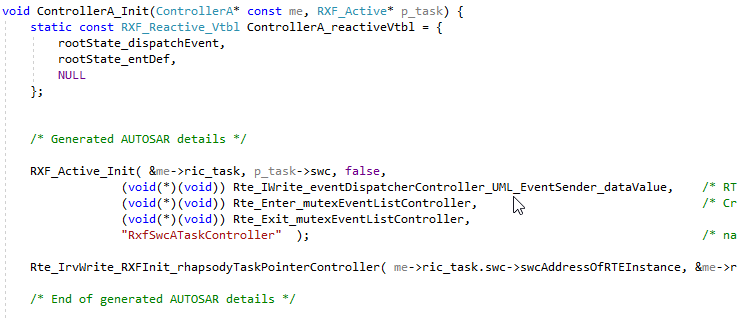
Active Classes
Code is generated to add AUTOSAR details to an internal task structure.
The RTE APIs used are functions which names are composed using the inter-runnable variables and exclusive areas.
To understand which inter-runnable variables belong to which runnables used for UML event dispatchers, the code generation needs two relations:
- the relation from runnable to the active class stereotyped by eventDispatcherActiveClass
to indicate the runnable is used as UML event dispatcher for that active class. See Profiles.
- the relation from runnable to interrunnableVariable stereotyped by variableAccess including if it is for reading or writing. See Profiles.
To understand which exclusive areas belongs to runnables used for UML event dispatchers, the code generation needs:
- the relation from runnable to exclusiveArea stereotyped by exclusiveAreaAccess
indicates the runnable used as UML event dispatcher is using this exclusive area for reading and writing. See Profiles.
On the the ARXF-CP Configuration Code Generation tab you can
specify which RTE function must be called if a UML event is added to the event queue of an active class.
Use an empty property ARXF_CP::CodeGeneration::RTEtriggerUMLeventDispatcherActiveClass if the runnable is triggered already (for example cyclic) depending on the RTE configuration for this runnable.
Runnables
An SW-C modelled in Rhapsody using the ARXF-CP has different kinds of runnables:
- the ‘init’ runnable to initialize the instance of SW-C including ARXF-CP.
The ‘init’ runnable itself does not use RTE APIs, but during initialization of SWC (including active classes) and ARXF-CP,
code is generated where function pointers towards RTE APIs are passed.
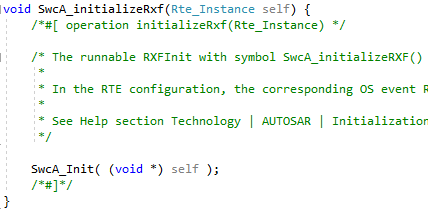
- an ‘eventDispatcher’ runnable which processes all UML events for a task and serves as heartbeat for the ARXF-CP. It must be triggered by the RTE at a regular interval:
You can modify the code. The default code looks like below, where string patterns are replaced:

ARXF-CP Event Dispatchers
Some runnables are used as UML event dispatchers: such runnable processes the UML event queue for that task.
An SWC uses its own task and each active class uses its own task.
When a UML event is added to the event queue of another task, that task must be triggered by the RTE in case that task is sleeping.
For this, you must use a function provided by the RTE if that runnable is not already triggered for example:
- cyclic by the RTE or when data has arrived. If a UML eventDispatcher runnable is called already by the RTE, you do not need to trigger it when a UML event has been added.
Of course, the frequency of the RTE trigger and how often UML events are processed by that runnable have impact on the
Realtime behavior when using tm() timeouts in the class which is related to the UML event dispatcher.
You can specify the name of the RTE trigger on the the ARXF-CP Configuration Code Generation tab. The name of the RTE trigger is passed as function pointer to a RXF_Active_Init() generated to initialize an SWC or active class.
AUTOSAR Ports
Code for AUTOSAR ports is not generated automatically; you must use the RTE APIs provided in the RTE contract of your SWC.
However, the Helper interface2runnable can be used to add a runnable to your SWC including a portAreaAccess dependency
to a receiver port or a server port.
When generating a mini-RTE for your model, the rootcomposition is used to understand
which SWC prototypes are connected via what AUTOSAR ports to other SWCs. During the generation of the mini-RTE,
runnables which have portAccess dependencies are used to implement Client/Server and/or Sender/Receiver communication.




